Summary
- This blog explores the fundamental concepts of economics, including the problem of scarcity, the need for choice-making, and the definition and importance of opportunity cost. Read on to become an expert in the field.
Economics is the study of how societies allocate scarce resources to meet unlimited wants and needs. At its core, economics is about understanding the fundamental economic problem of scarcity and the choices that individuals, firms, and governments must make in response to it.
Scarcity is the idea that resources are limited and that there is never enough to satisfy all wants and needs. This forces people to make choices about how to allocate their resources. For example, an individual must choose between buying a new car or saving for a down payment on a house. A firm must choose between investing in new technology or expanding its marketing efforts. A government must choose between spending on education or defense.
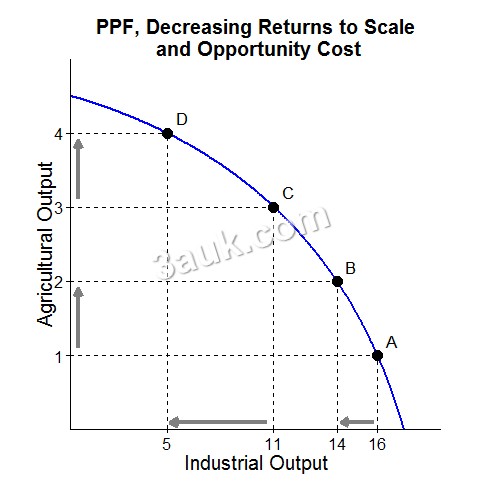
The choices that individuals, firms, and governments make in response to scarcity give rise to the concept of opportunity cost. Opportunity cost is the value of the next best alternative that must be given up in order to pursue a particular choice. In other words, it is the cost of the most valuable opportunity forgone.
For example, if an individual decides to buy a new car, the opportunity cost is the value of the down payment on a house that they could have saved. If a firm invests in new technology, the opportunity cost is the potential sales and profits that could have been gained from expanding its marketing efforts. If a government spends on education, the opportunity cost is the potential security and defense benefits that could have been gained from spending on those areas instead.
The basic questions of resource allocation are central to economics. How should resources be allocated to meet unlimited wants and needs? Who should make these decisions? How can we ensure that resources are used efficiently and effectively? These questions are the foundation of microeconomics and macroeconomics, two branches of the discipline that focus on understanding how markets and the economy as a whole work.
In conclusion, the concepts of scarcity, choice, and opportunity cost are fundamental to understanding economics. They are central to the study of how societies allocate resources to meet unlimited wants and needs and form the basis for exploring the basic questions of resource allocation.
Keywords: economics, scarcity, choice, opportunity cost, resource allocation, microeconomics, macroeconomics, markets, economy.
Important economic concepts: scarcity, choice, opportunity cost, resource allocation, markets, efficiency.
Read more on related topics here