Content
- Topic Questions – EASY: Production Possibility Curve
- Topic Questions – HARD: Production Possibility Curve
shape of the PPC: constant and increasing opportunity costs
The shape of the PPC is determined by the concept of opportunity cost.
- The slope of the PPC at any point represents the opportunity cost of producing one more unit of the good on the horizontal axis.
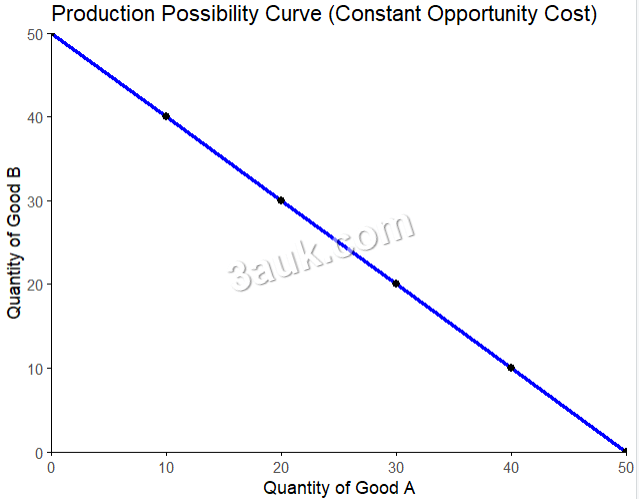
- Constant opportunity cost PPC is a straight line, which represents that the opportunity cost of producing one good is always the same.
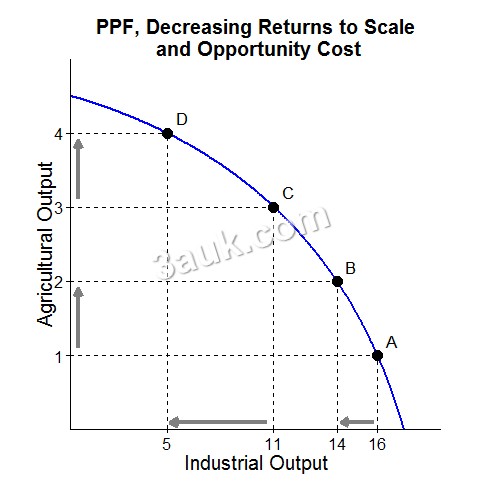
- Increasing opportunity cost PPC is bowed outward from the origin, which represents that the opportunity cost of producing one good increases as more of it is produced.
- reflect decreasing return to scale
causes and consequences of shifts in a PPC
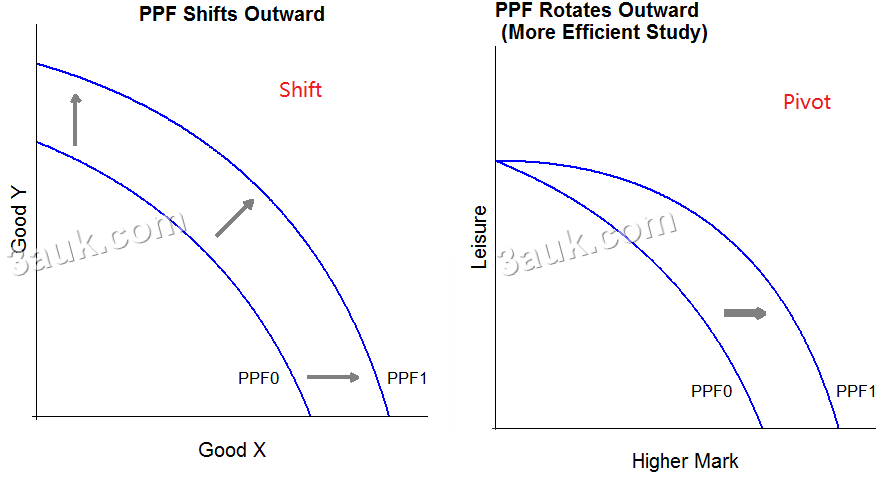
- Causes of shift
- New resources, e.g. new mine
- Increased labour supply, e.g. more immigrants
- Improvements in human capital, e.g. better education
- Improved resource management
- Privatisation
- New resources, e.g. new mine
- Pivots: one product's technology improves
significance of a position within a PPC
- Points inside the curve indicate unemployment and points on the curve show full employment.
- too much waste in production
- some resources not used
Join the conversation