Content
Syllabus
find the discriminant of a quadratic polynomial ax^2+ bx + c and use the discriminant
- e.g. to determine the number of real roots of the equation
ax^2 + bx + c = 0. Knowledge of the term ‘repeated root’ is included.
Determinant
- The discriminant of a quadratic equation is a value calculated from the coefficients of the equation that provides information about the nature of the roots (or solutions) of the equation.
\Delta = b^2 - 4ac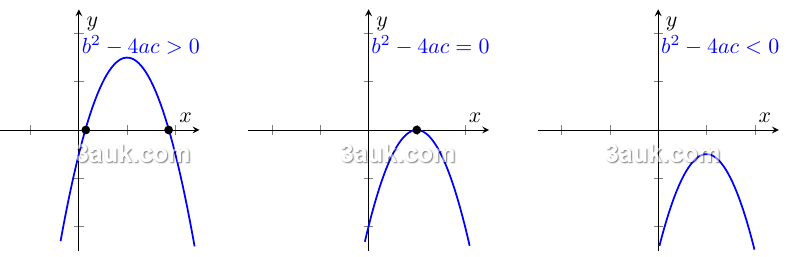
- The value of the discriminant determines the number of real roots of the equation and their type. Specifically:
- If the discriminant is positive, the equation has two real roots that are distinct and different.
- If the discriminant is zero, the equation has exactly one real root that is a repeated root.
- If the discriminant is negative, the equation has two complex roots that are conjugates of each other.
Join the conversation