In Economics, joint supply occurs when two or more products are produced simultaneously from the same production process, such that an increase in the supply of one good automatically increases the supply of the other(s).
- Example: Beef and leather are in joint supply, as slaughtering cattle for meat also yields hides for leather production.
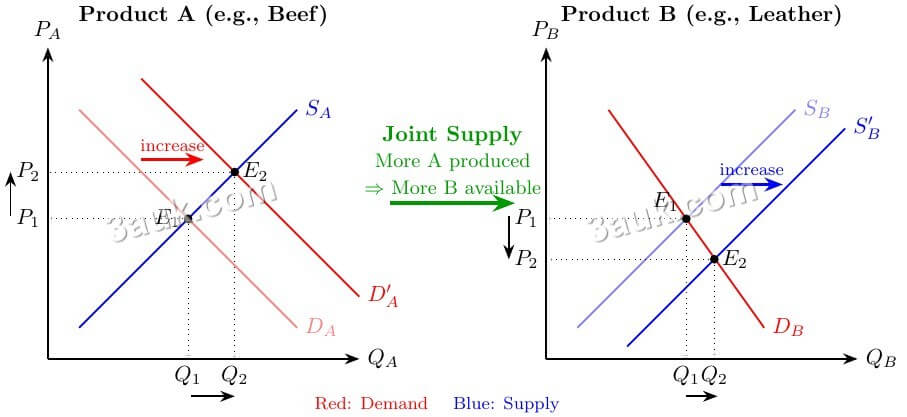
Check Mastering Joint Supply – A Level Economics (Beef & Leather) for more details.