Price elasticity of demand (PED) measures the responsiveness of the quantity demanded for a good or service to a change in its price.
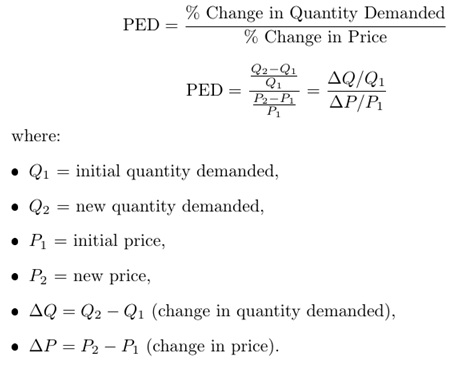
Magnitude of PED
- A PED value greater than 1 shows that demand is price elastic: a small percentage change in price causes a larger percentage change in quantity demanded.
- Perfectly elastic demand occurs when even a tiny price change leads to an infinite change in quantity demanded, giving a PED coefficient of infinity.
- A PED value less than 1 indicates price inelastic demand: a small percentage change in price results in a smaller percentage change in quantity demanded.
- Perfectly inelastic demand happens when a price change has no effect on quantity demanded, resulting in a PED coefficient of zero.
- A PED value of 1 signifies unit elastic demand: the percentage change in quantity demanded equals the percentage change in price.
Factors influencing the magnitude of PED
- Availability of substitutes
- Proportion of income spent on the good
- Whether the product is a necessity or a luxury
- Time period considered, as changing habits or suppliers may take time