- Topic Questions (MCQ – EASY): Developing and Developed Countries
- Topic Questions (MCQ – HARD): Developing and Developed Countries
income distribution
The Gini coefficient is a widely used measure of income inequality within a country.
- It quantifies the extent to which the distribution of income deviates from perfect equality.
- The coefficient ranges from 0 to 1, where 0 represents perfect equality (all individuals have the same income) and 1 represents perfect inequality (one individual has all the income).
- The Gini coefficient is calculated by comparing the cumulative shares of the population against the cumulative shares of income.
- A higher Gini coefficient indicates greater income inequality.
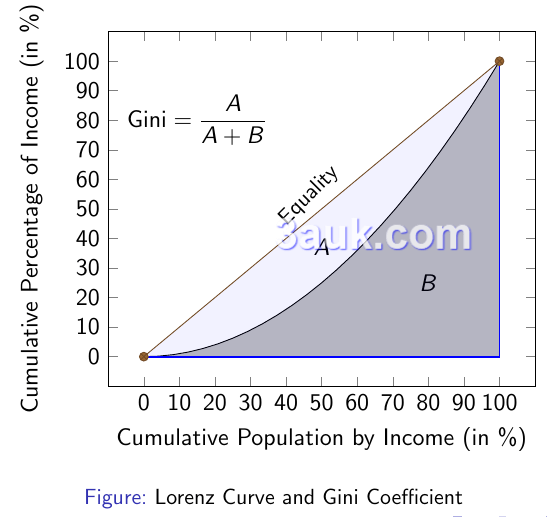
The Lorenz curve is a graphical representation of income distribution within a country.
- It plots the cumulative share of total income earned by the population against the cumulative share of the population, starting with the lowest-income individuals.
- The Lorenz curve allows us to visually analyze income inequality.
- If the Lorenz curve lies closer to the 45-degree line (perfect equality), it indicates lower income inequality.
- Conversely, if the curve is farther away from the 45-degree line, it suggests higher income inequality.
economic structure
The employment composition of a country refers to the distribution of labor across various sectors of the economy. It is commonly categorized into three sectors:
- Primary Sector: This sector includes activities related to natural resource extraction, such as agriculture, forestry, fishing, mining, and oil exploration.
- In less developed countries, the primary sector tends to employ a significant portion of the workforce.
- Secondary Sector: The secondary sector comprises manufacturing and industrial activities.
- It involves the transformation of raw materials into finished goods or intermediate products.
- As countries progress and industrialize, the secondary sector typically experiences growth, absorbing a larger share of the labor force.
- Tertiary Sector: The tertiary sector, also known as the services sector, encompasses a wide range of activities, including retail, healthcare, education, finance, transportation, tourism, and professional services.
- In more developed countries, the tertiary sector becomes the dominant employer, reflecting a shift toward service-oriented economies.
The composition of employment across these sectors evolves as countries progress. While developing countries often rely heavily on the primary sector, developed countries have a higher proportion of their workforce engaged in the secondary and tertiary sectors.
The pattern of trade refers to the types of goods and services that countries export and import. It evolves as countries move through different stages of development.
- Less Developed Countries: These countries typically export primary products, such as agricultural commodities, raw materials, and minerals.
- Their imports often consist of manufactured goods and capital-intensive products.
- Newly Industrialized Countries: As countries industrialize and move up the development ladder, their exports shift toward manufactured goods, including textiles, electronics, automobiles, and machinery.
- They may also begin to export some higher value-added products.
- Developed Countries: Developed countries tend to have a more diverse export base, including high-tech products, advanced machinery, pharmaceuticals, and services.
- They often have a significant presence in sectors such as finance, technology, and knowledge-intensive services.
The pattern of trade reflects a country's comparative advantage, which is influenced by factors like natural resources, technological capabilities, human capital, and infrastructure. As countries advance in their level of development, they tend to diversify their exports, focusing on higher value-added goods and services.